12 ways to fix “no sound” on your computer
You can fix the “no sound” error on your computer in a few different ways, such as checking your auxiliary connections or updating your drivers with a reliable driver updater tool. Here are the best ways to fix the sound on your computer:
1. Check your hardware and cable connections
One of the easiest ways to fix your computer's sound is to check that all your cables are connected properly. Loose or faulty cables, disconnected speakers, or malfunctioning audio jacks can affect sound output.
Check if your speakers are on
Ensure your speakers are firmly plugged into a power source or fully charged (if needed) and connected to your PC. If your speakers have a power button, make sure it’s switched on.
Disconnect your headphones
Sound issues can be caused by headphones that have incorrect settings, loose connections, low volume, disabled devices, driver problems, or Bluetooth issues. Disconnecting your headphones may restore sound to your PC’s integrated speakers.
Here’s how to disconnect your headphones:
-
Wired headphones: Unplug them from the AUX (3.5mm) jack or USB port.
-
Wireless (Bluetooth) headphones: Click the Bluetooth icon in the taskbar or go to Settings > Bluetooth & devices. Find your headphones and click Disconnect or toggle off Bluetooth.
Once disconnected, Windows should switch audio back to your built-in speakers automatically.
Reconnect loose audio cables
A loose cable can disrupt the connection between your PC and speakers or headphones, resulting in poor or no sound. Try reconnecting the audio cable that links your speakers to the PC, or the headphone jack if you're using headphones.
Gently unplug and replug the cable at both ends to ensure a firm connection, making sure it’s securely connected to the correct audio-out jack or USB port. If it still feels unstable, try using a different port. Once reconnected, test the audio to see if the issue is resolved.
Try a different USB port
Switching ports can help rule out a faulty port or connection issue. This can also help you rule out possible driver or connectivity problems with the original port. Look for an alternative USB port (for USB-connected devices) and try both USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 ports, if available. If your laptop has limited USB ports, consider using a USB-C extension hub for more connectivity options.
Plug into the correct jack
If your headphones use an AUX port (3.5mm jack), check they’re plugged into the correct one. Some newer Windows PCs have a single combo port for both audio output and mic input, identified by a headset icon. But on others, the audio-out jack for speakers or headphones is typically marked with a headphone symbol. Plugging into the mic jack — usually pink with a mic icon — won’t produce sound.
Turn your volume up high
If your volume is set too low or muted, the audio signal won’t be strong enough to be heard, even if everything’s connected properly.
The quickest way to turn the sound up on Windows 11 is to adjust the volume using your keyboard if it has volume buttons. Press the volume up button to increase the sound (usually a speaker with three sound waves).
Alternatively, you can use the Windows taskbar to adjust the volume:
-
Click the speaker icon on the right side of the taskbar and slide the volume bar to the right to increase the volume.
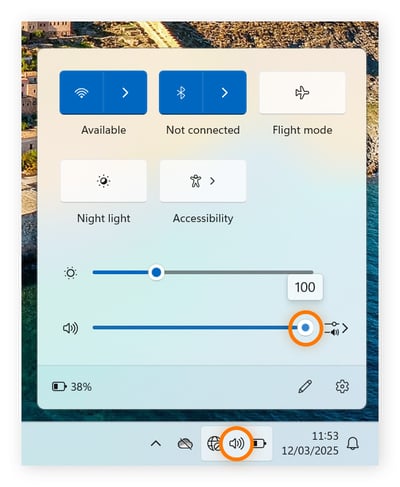
-
If your volume is still low or not working, right-click the speaker icon, select Sound settings, and adjust the volume for your device or apps individually.
Unmute all audio components
Unmuting all audio components on your PC, such as the system output, individual apps, and connected devices, can help restore sound if the audio source is muted. Check your PC’s main volume settings, as well as sound controls for apps and external devices like speakers or headphones.
Adjusting the volume up or down usually turns off the mute automatically. But there are other options you can try if this doesn’t work:
-
Unmute system volume: Click the speaker icon in the taskbar and check if it’s muted, click the mute symbol, and drag the volume slider to a higher level if necessary.
-
Unmute external devices: If you’re using speakers or headphones with built-in volume controls, check for a mute button and turn up the volume.
-
Check app volume: Open the app you’re using (e.g., Spotify, YouTube, Zoom, or media player) and make sure it’s not muted within the app’s settings.
-
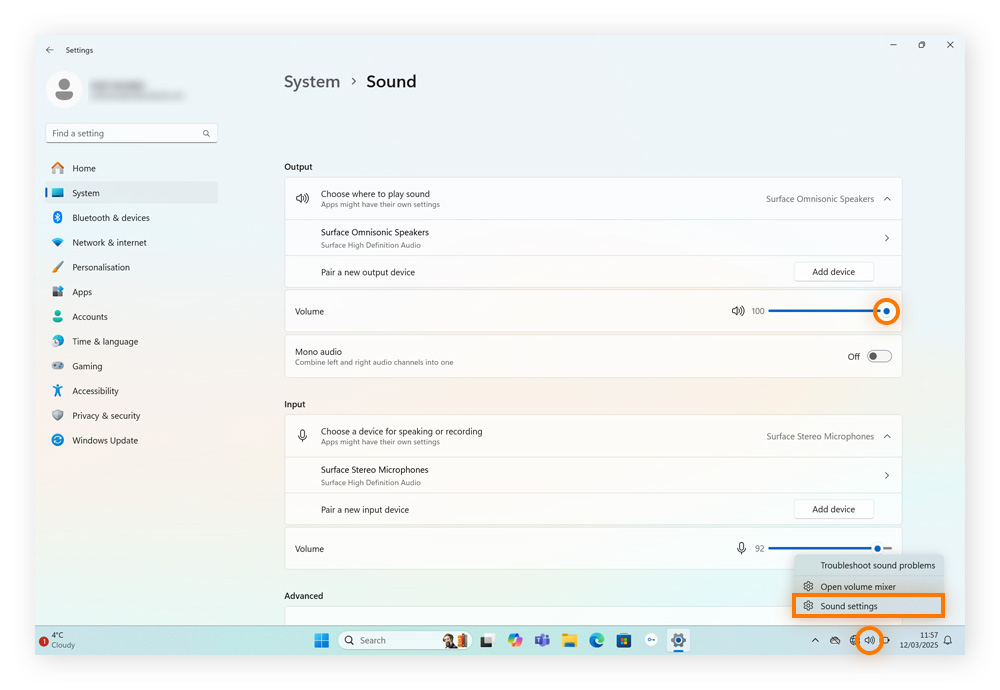
Check Volume Mixer: Right-click the speaker icon, select Open volume mixer, and ensure all apps and devices are unmuted.
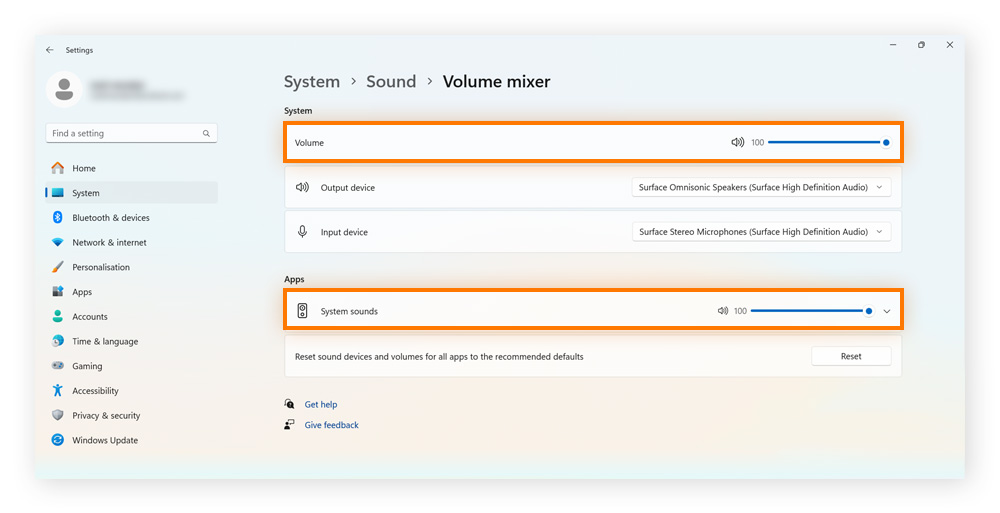
Check for disabled output devices
Disabled output devices are speakers, headphones, or other audio devices that have been turned off in Windows settings. If your primary audio device is disabled, Windows won’t send sound to it, and you won’t be able to hear any output.
Here is how to enable output devices:
-
Right-click the speaker icon in the taskbar and select Sound settings.
-
Scroll to the Output section and click Manage sound devices.
-
Under Output devices, look for any device labeled Disabled, click on the disabled device, and select Enable.
If the problem is not resolved, go back to Sound settings, select your output device, and click Set as default if necessary. Play audio to check if the issue is resolved.
2. Run Windows’ audio troubleshooter
For persistent sound problems, run the audio troubleshooter in Windows. This can help diagnose and fix common sound issues by automatically detecting problems with your audio devices, drivers, or settings.
As of 2025, Microsoft has moved several Windows troubleshooters from the legacy Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) to the Get Help platform to provide a more modern support experience.
Here’s how to run the audio troubleshooter via Get Help (Windows 11 or newer):
-
Press the Windows icon + S on your keyboard, type “get help” and hit Enter to open the app.
-
Type “Fix sound problems” in the Get Help search bar and hit Enter.
-
Follow the on-screen instructions to diagnose and resolve audio issues.
Alternatively, you can go to Start > Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other Troubleshooters > select the audio troubleshooter.
For devices running Windows 11 version 22H2 and older, follow these steps to run the audio troubleshooter via system settings:
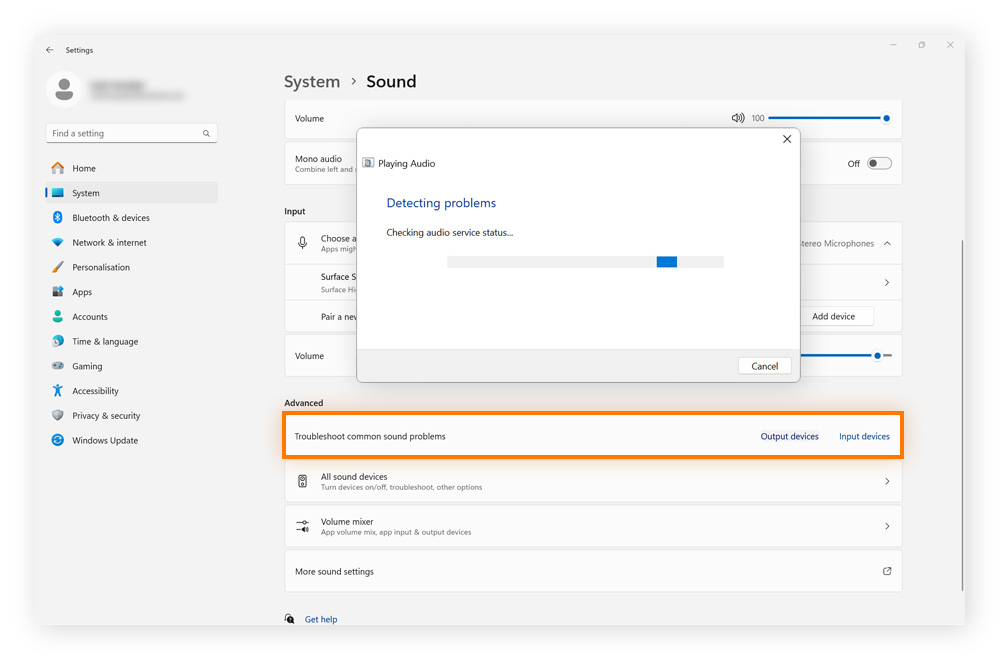
The audio troubleshooter on Windows can help solve issues with your sound not working for both input and output audio devices. If sound problems continue, contact your computer or sound card manufacturer.
3. Complete all Windows updates
Completing Windows updates can help fix sound issues because updates often include bug fixes, driver updates, and system improvements that resolve compatibility problems with audio devices.
Here’s how to check and install Windows updates:
-
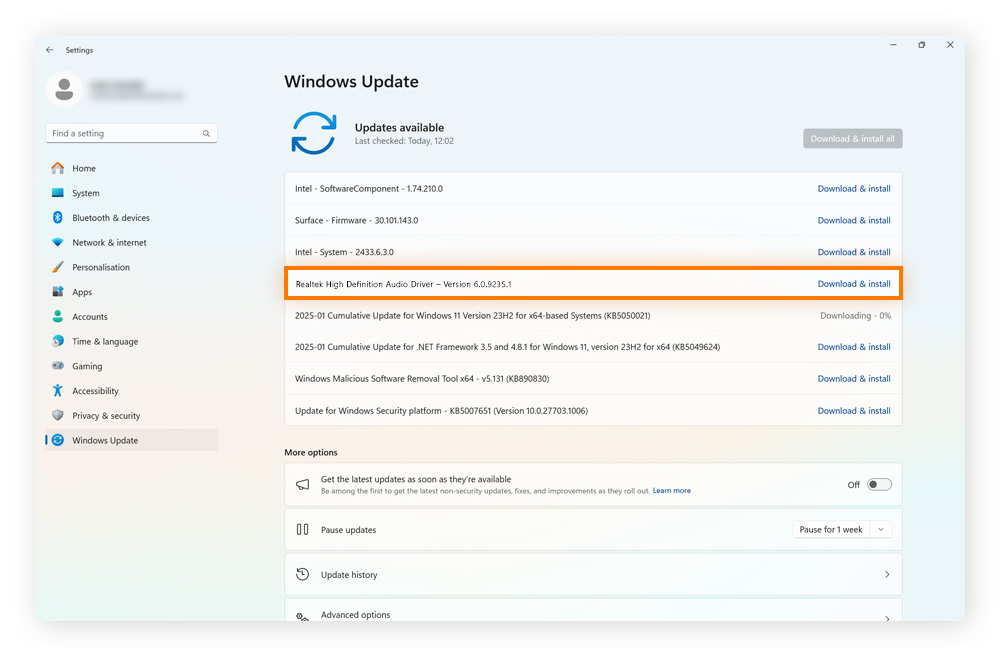
Open Windows Settings and click Windows Update > Check for updates.
-
If an update is available, click Download & install and wait for the process to complete. If prompted, click Restart now.
4. Check for apps causing audio conflicts
Some programs on your PC may interfere with your audio by taking exclusive control of the sound device or applying their own audio settings. This can lead to conflicts, muted output, or distorted sound — even if your system appears to be working normally.
Here’s how to check for audio conflicts:
-
Close unnecessary apps. Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc, go to the Processes tab, select the app, and click End Task to stop music players, streaming apps, or communication tools such as Microsoft Teams or Skype.
-
Check app-specific audio settings. Some apps, like Zoom or Discord, have their own audio settings. Make sure the correct output device (headphones/speakers) is selected within the app.
5. Check the audio settings on your computer
To manage your audio settings quickly on Windows 11, press the CTRL + V + Windows buttons on your keyboard to access your sound settings. Alternatively, you can right-click the speaker icon in the Windows taskbar and select Open Sound settings.
From there, you can see which device is selected for audio output. If you’re not hearing sound, the wrong device may be selected — try switching to another option, like your speakers or headphones, to restore audio.
6. Restart your computer or speakers
If there’s still no sound on your computer, restart your PC and speakers. That might be all it takes to fix your audio issues.
Restart your PC
Restarting your PC can resolve sound issues by clearing temporary glitches, reloading audio drivers, and resetting system configurations. It gives Windows a fresh start and can fix problems like unresponsive audio devices or incorrect settings.
To restart your Windows 11 PC, click the Start button (or press the Windows key), select the Power icon, and choose Restart.
Restart Windows Audio Service
Windows Audio Service is a set of background processes that manage how sound is handled on your PC. It ensures communication between your audio devices, drivers, and applications. If the service stops or is misconfigured, it can cause sound issues or complete audio loss.
Here’s how to restart Windows Audio Service:
-
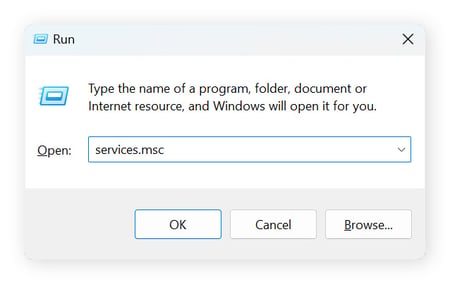
Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog, type services.msc, and click OK.
-
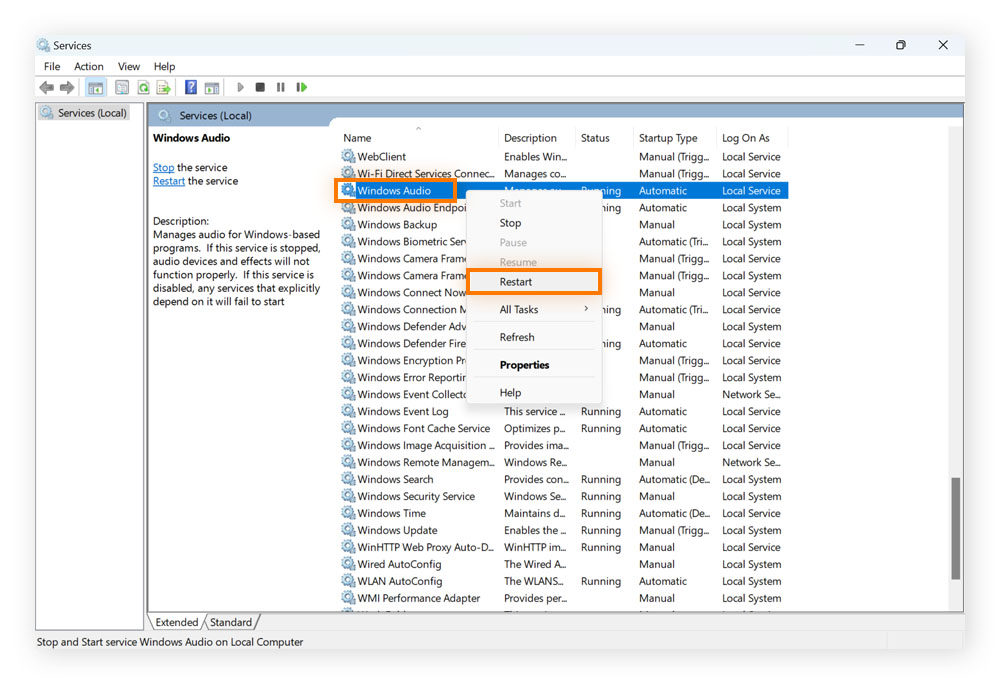
Scroll down the Services window, right-click Windows Audio, and select Restart.
Restart your speakers
Restarting your speakers can help fix sound issues by resetting their internal hardware and re-establishing a clean connection with your PC. Problems like power glitches, software conflicts, or unresponsive hardware can often be resolved this way.
If your speakers have a power button, switch them off. For USB-powered speakers, unplug them from the USB port. If they use an external power source, disconnect them from the outlet. Wait 10–15 seconds before reconnecting, powering back on, and making sure they’re properly connected to your PC via AUX, USB, or Bluetooth.
7. Change your audio output device
If your audio still isn’t working, try changing your default sound device in the audio settings. The default determines which connected device (e.g., speakers, headphones, or external interfaces) Windows uses for sound output and input.
If you have more than one audio device connected, manually selecting the right one helps ensure sound plays through the correct channel. It also keeps things consistent across apps and can often resolve sound issues caused by the wrong device being selected.
Swap to a different connected device
-
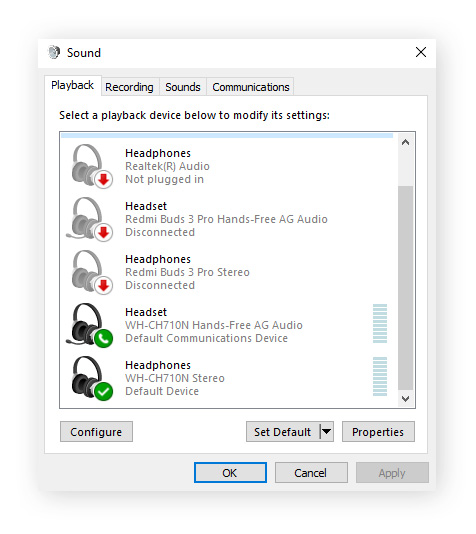
Right-click the speaker icon in the Windows taskbar and select Sound settings.
-
Click More sound settings and navigate to the Playback tab.
-
Select your preferred audio device and click Set Default > OK.
Connect a new audio device
Connecting a new audio device — such as different speakers or headphones — helps diagnose whether the issue is with your PC’s settings or the original audio device itself. If the new audio device works, it confirms the problem was with the previous audio device and not your PC.
-
Connect wired devices via the AUX (3.5mm jack), USB, or HDMI port.
-
For Bluetooth devices, go to Settings > Bluetooth & devices > Add device and select Bluetooth.
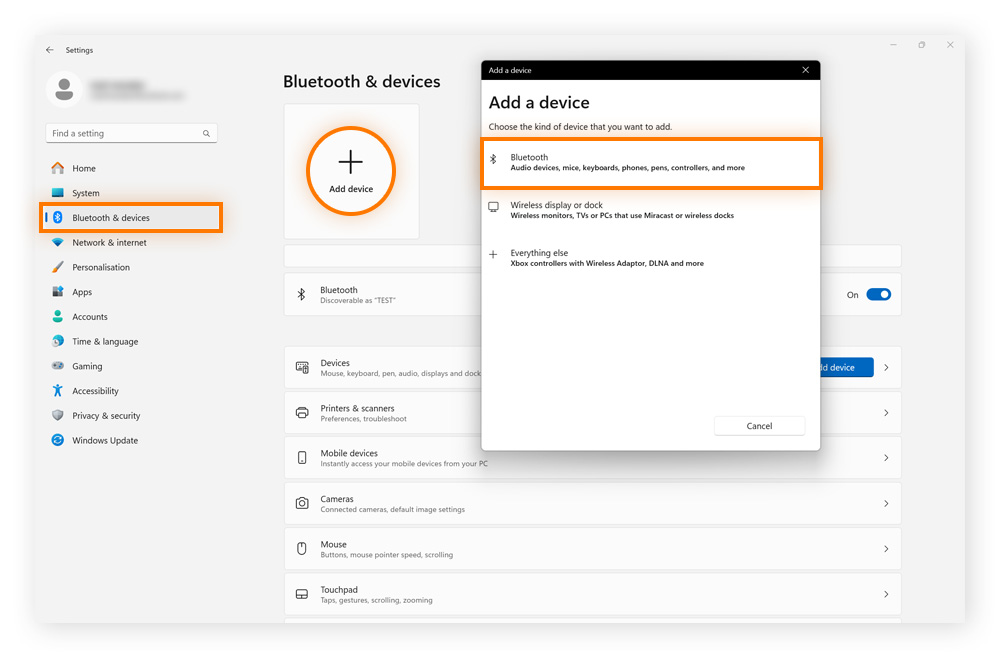
If the new device works, it means the original device might be faulty, improperly connected, or disabled in settings. Knowing this helps you pinpoint the cause and decide whether to fix or replace the original audio device.
8. Install or update your audio or speaker drivers
Installing or updating your audio or speaker drivers helps ensure your PC can communicate properly with its sound hardware. When drivers are outdated or corrupted, you may experience issues like distorted audio, lag, or complete loss of sound. Updating them can resolve bugs, fix compatibility problems, and restore normal audio performance caused by driver-related conflicts or errors.
Automatically update your drivers
Updating your sound drivers automatically with a dedicated PC optimization tool can help you quickly fix your sound issues and boost your computer’s overall performance.
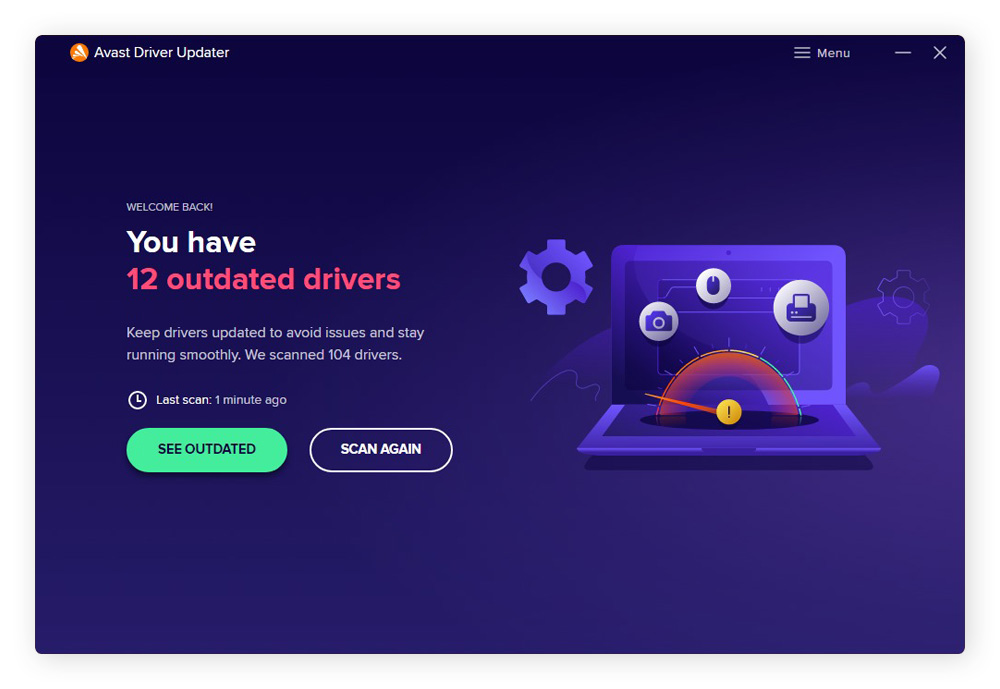
Here’s how to update your drivers automatically with Avast Driver Updater:
-
Download and install Avast Driver Updater.
-
Click Scan Drivers to check your graphics card and the rest of your system for available updates
-
Then, simply click Update All, or select the drivers you want to update individually from the list of outdated drivers.
Manually update your drivers
You can also update audio drivers manually via Windows Update on Windows 10 and 11. Simply open the Windows Start menu and select Settings > Windows Update > Check for updates.
Windows Update doesn’t let you select individual drivers — it installs a bundled package that includes the latest available Windows driver updates. Keeping all drivers up to date, not just audio, helps maintain performance and ensure your PC runs at top speed with the latest fixes and improvements.
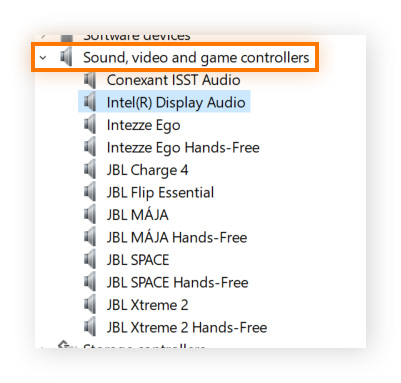
You can also update your audio drivers via Device Manager:
-
Type device manager into the Windows search bar and hit Enter to open Device Manager.
-
Expand Sound, video and game controllers, right-click the audio card you want to update, and select Update driver.
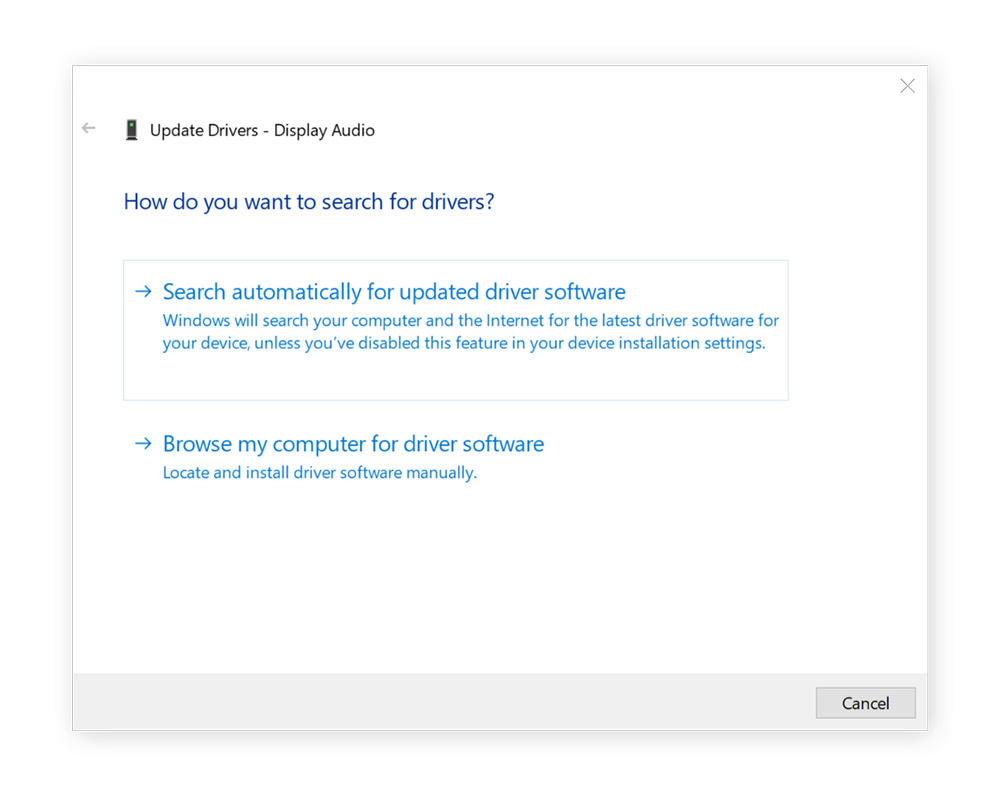
-
Select Search automatically for drivers. If Windows doesn’t find anything, you can download the latest drivers from your sound card manufacturer’s website, then return to the Update Driver window and select Browse my computer for drivers.
9. Disable audio enhancements
Third-party speaker manufacturers sometimes use audio enhancements to make their devices sound better. But if the enhancements aren’t configured properly, that can explain why your desktop computer or laptop speakers aren’t working.
Here’s how to disable audio enhancements and fix your computer sound:
-
Right-click the speaker icon in the taskbar and select Sound settings.
-
Scroll down and click More sound settings, and select the Playback tab.
-
Right-click your audio device and select Properties.
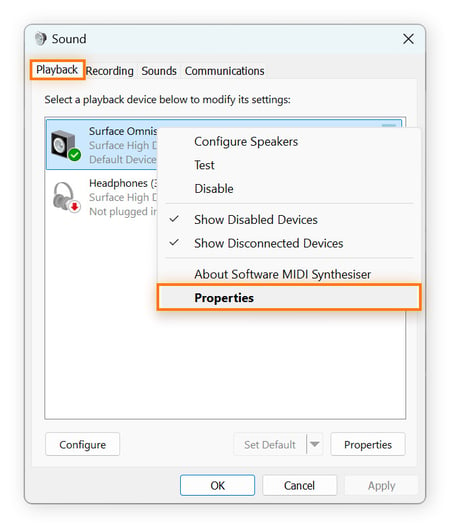
-
Go to the Advanced tab, deselect Enable audio enhancements, and click OK.
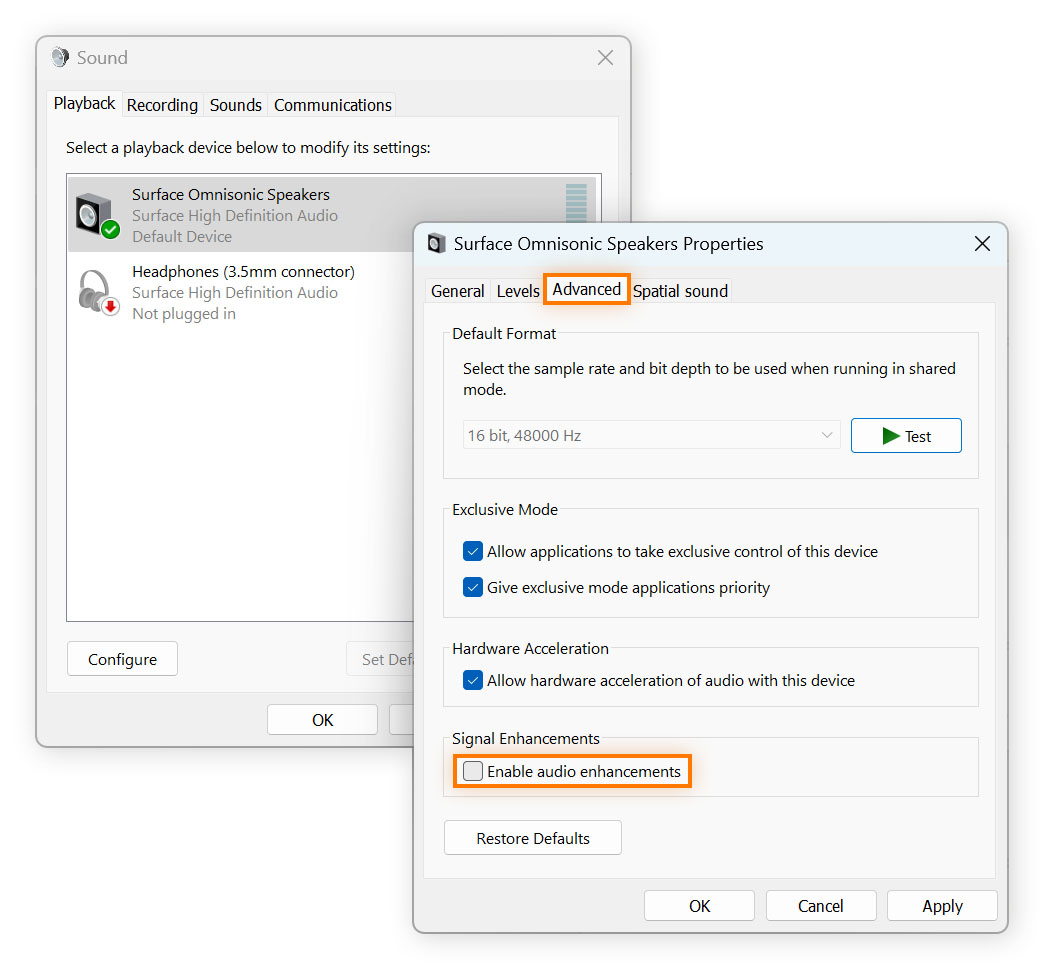
10. Test other audio formats
If you have an audio file on your Windows PC that is not producing sound, test different audio formats to help identify compatibility issues between the file and the playback software. Some formats may not be supported or may require specific codecs (coding-decoding systems), leading to playback problems.
Windows 11’s Media Player supports a range of audio formats, each with different levels of quality, compression, and compatibility. The most common audio files are in MP3, AAC, or M4A due to their balance of quality and file size.
By trying various formats, you can determine if the issue is format-specific or related to other factors.
-
MP3: The most common format and widely supported. Good for general use.
-
FLAC: Lossless compression. High quality and larger file size.
-
AAC: Better compression than MP3, with improved sound quality. Commonly used in streaming (e.g., Spotify).
-
M4A: Similar to AAC, it is of good quality with moderate file size.
-
WAV: Uncompressed, high quality, and large file size. Commonly used in professional audio editing.
-
WMA: Microsoft’s alternative to MP3, it is mostly used on older software. Lossy or lossless. Not widely supported outside of Windows.
-
AMR: Designed for voice recordings — optimized for speech, but low quality.
-
OGA/OGG: Open-source alternative to MP3. Better quality at similar file sizes.
-
OPUS: Highly efficient and ideal for real-time applications like VoIP or streaming.
Here’s how to change the audio format of a file on Windows 10 and 11:
-
Download, install, and open a reputable audio conversion software, like MediaHuman Audio Converter.
-
Drag and drop the desired audio file into the program window or use the Add button to select the file.
-
Select your desired output audio format, click Convert or Start (depending on your audio converter), and select Download file.
-
Locate and test your converted audio file.
11. Update the BIOS
If your computer sound still isn’t working or your computer keeps crashing, you may need to update your BIOS/UEFI to resolve hardware incompatibility issues or software updates.
The BIOS/UEFI is the firmware that helps your computer start up and communicate with hardware such as your headphones and speakers. Updating it can fix audio compatibility issues and ensure your system runs the latest software smoothly.
Here’s how to update your BIOS/UEFI on Windows 11:
-
Press the Windows icon + R, type msinfo32, and press Enter.
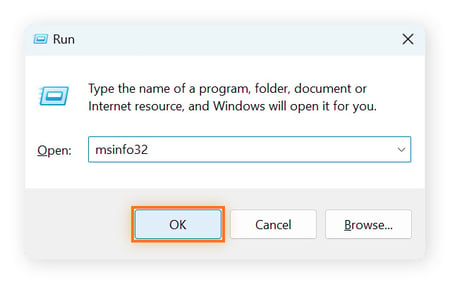
-
Navigate to BIOS Version/Date and note the version.
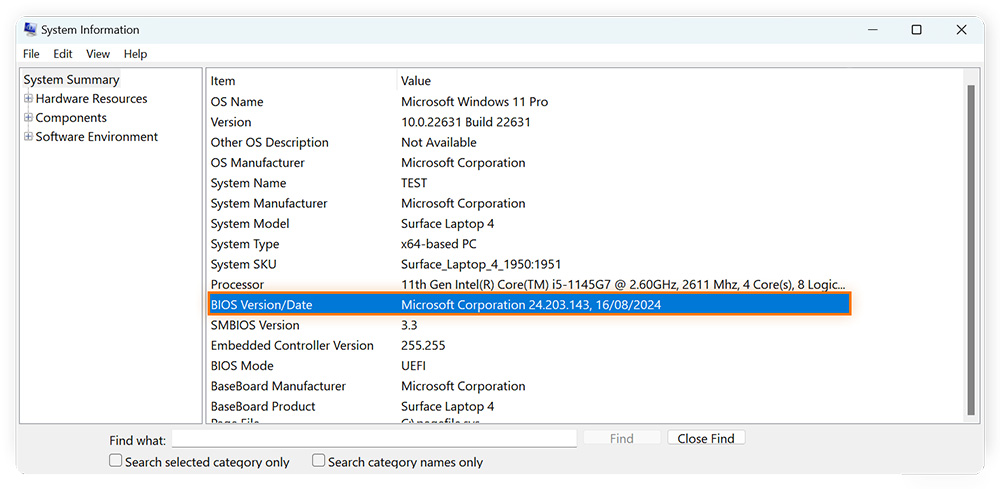
-
Go to the official website of your motherboard’s manufacturer, search for BIOS updates using your model number, and compare your current version with the latest one available.
-
Download the official update file if an update is available and follow the manufacturer’s installation guidance.
12. Seek professional advice
If your sound still does not work, try consulting a certified technician or IT expert who has the knowledge and tools to diagnose and fix complex computer issues. A professional can identify deeper issues — such as hardware failures, driver conflicts, or motherboard problems — that require advanced solutions.
A professional can help fix your sound issues by providing:
-
Expert diagnosis: Professionals use specialized tools to detect issues beyond standard troubleshooting.
-
Advanced repairs: They can replace faulty components, update firmware, or reinstall system software.
-
Guaranteed solutions: Unlike trial-and-error fixes, professionals provide reliable repairs to prevent recurring issues.
Why can't I hear anything on my PC?
If you can’t hear anything on your PC, the most common reasons are muted or low volume, the wrong output device selected, and outdated or corrupted audio drivers. Checking your settings and updating drivers can often restore sound quickly.
-
Muted or low volume: Your system, app, or device volume may be muted or too low.
-
Wrong output device: The audio may be playing through a different device, like a disconnected monitor or Bluetooth speaker.
-
Loose or faulty connections: Cables for wired speakers or headphones may be loose or damaged.
-
Disabled or disconnected audio device: Your audio device might be disabled in Windows settings.
-
App-specific issues: Apps with their volume controls may be muted or set to a different output.
-
Outdated or corrupted drivers: Audio drivers may need to be updated or reinstalled.
-
Windows audio services not running: The system’s audio services may have stopped or encountered an error.
-
Hardware issues: The speakers, headphones, or sound card might be damaged or malfunctioning.
-
Bluetooth interference: Wireless audio devices may not be paired properly.
-
Windows updates or software conflicts: A recent update or two programs not working well together — like an audio driver clashing with a new app — could be messing up the sound settings.
Update your drivers automatically with Avast
There are plenty of potential reasons why you have no sound on your computer — and one of the most common is an outdated or faulty audio driver. Thankfully, this issue is avoidable and easy to solve.
Simply download Avast Driver Updater to scan for faulty or old drivers, then update them at the click of a button. Performance experts designed this tool to keep all your drivers working properly — not just your sound drivers, but your graphics card, network drivers, and much more. Try Avast Driver Updater for free today.





















/The-best-driver-updater-software-for-WindowsThumb.jpg)


